Suppose you’re tasked with automating a factory or warehouse. Your goal is to efficiently transport products from one location to another, and pneumatics emerges as a potential solution. However, pneumatic systems require significant plumbing, typically in the form of synthetic plastic or rubber tubing or hose. But with a plethora of pneumatic hose options, how do you select the best one for your specific needs? Here are the key factors to contemplate when choosing a pneumatic hose.

Image courtesy of AutomationDirect
The first consideration should be the flow rate of your components, actuators, and the pneumatic hose itself. For instance, high-volume production lines or quick movement of large actuators necessitate pneumatic tubing with high flow rates to ensure sufficient supply to your machinery.
Material composition should also be taken into account, as it influences flexibility, durability, weight, and compatibility with external variables. In food and beverage applications, for example, the tubing material must be food-safe, leaving no toxic residue. Certain materials like PVC, which might contaminate products, should be avoided.
Polyurethane hose is frequently used in automation and robotics due to its exceptional flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and UV rays. It’s suitable for compressed air systems and food and beverage applications, such as CO2 lines in soft drinks.
Nylon tubing, known for its high-pressure resistance, excellent flexibility, and durability, is often used in pneumatic systems. It’s also apt for compressed air systems and in the food and beverage industry, specifically for CO2 lines in beer.
Polyethylene, due to its flexibility, lightweight, and chemical and impact resistance, is suitable for a range of pneumatic applications. Teflon, resistant to high temperatures and chemicals, is particularly beneficial in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage industries.
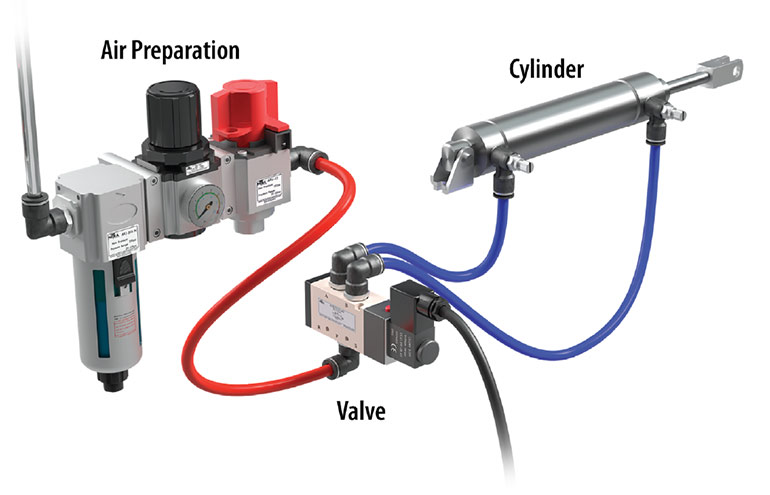
Image courtesy of AutomationDirect
The pressure rating of the pneumatic hose is another critical factor to consider. Not all tubing can resist the same pressure, especially in challenging environments subjected to high or low temperatures or exposure to chemicals. Ensure you select the hose based on its working pressure rather than its maximum pressure.
Size and length of the pneumatic tubing also need to be considered. Longer tubes result in more cumulative pressure drop, potentially requiring a larger size. Also, consider the mobility of the hose— rigid hoses like Teflon may not last as long in high-motion applications compared to more flexible options like nylon.
Lastly, balance the aforementioned factors with cost considerations. Pneumatic tubing is available at various price points. The goal is to find a tubing that fits within your budget and satisfies your requirements. Buying in bulk often leads to discounts. Color-coding your tubing can also be beneficial. While there are no industry standards, red is often used for pressure lines and blue for atmosphere.





